Summary
Learn about the different types of Artificial Intelligence, the three lenses through which to view and learn about AI, and learn more about AI Unwrapped on September 7th with Charlotte Dugan.
AI has quickly become a hot topic. It is everywhere from the Hollywood writer’s strike to the predictive text in your email program. Even if you aren’t consciously using AI, you are using AI. So what exactly is AI? According to IBM, “Artificial Intelligence leverages computers and machines to mimic the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of the human mind.” This is accomplished by programming an algorithm to perform a specific task, usually make a decision, based on a certain data set. That data can be anything from a small and specific set of data for research purposes or all of the information it can access on the internet.
- Weak or Narrow AI is clearly defined as AI programmed to perform a specific task or solve a specific problem. This can range from the shuffle on your playlist, the predictive text on your phone or email, Siri and Alexa, to the personalized ads you see, even self-driving cars. You probably interact with Weak AI hundreds if not thousands of times a day.
- Generative AI is geared towards generating content. It combines algorithms, large language models, and deep-learning neural networks to generate new content. PlaygroundAI, ChatGPT, and Bard are a few examples of these and the ones we tend to find the most useful and problematic for schools.
- Strong or General AI is human-like AI. This is where things get a little muddy. Some define the human-like qualities need to be strong AI as the ability to create, making Generative AI Stong AI. Some define human-like qualities needed to be Stong AI as reasoning. If you are a Star Wars fan this might look like R2D2 while if you are a Star Trek fan it might look more like Data.
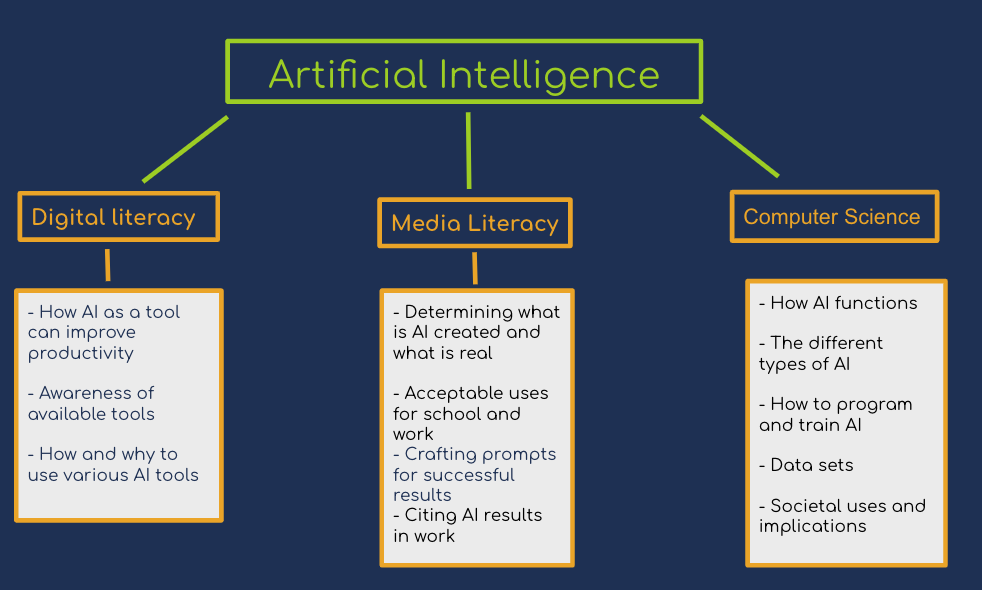
When learning about AI either for yourself or for your students it is important to consider your approach through one of three lenses; Digital Literacy, Media Literacy, and Computer Science. Using these lenses can help you focus your purpose and direction and better tie to existing content needs and standards.
- Digital Literacy focuses on how and why to use AI and various AI tools.
- Media Literacy focuses on what is an acceptable use of AI in school and work, how to cite AI results, and how to determine what content or information may be genuine or “fake” or AI created.
- Computer Science focuses on the different types of AI, how to program and train AI, the societal implications, and the data sets used in AI.